Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation - Deep overview
Electrical energy and human health:
Electric stimulation to control pain was used in ancient Rome, 63 AD. This is the original history of TENS.The strong development stage of TENS started from the time of scientific development (the scientific period prevailed over religion), which is from the 16th century until now.
See more about TENS: TENS: Stimulates Transdermal Nerves
Research and development of science-based TENS has created a new branch of physiotherapy: "Cranial electrotherapy stimulation"(CES).
What is Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES)?
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of nerve stimulation that provides a small electric current - pulse current - alternating through electrodes on the head.CES generates pulse current:
- noninvasive
- transcranial
- Apply a specific amplitude, frequency and waveform to the patient.
CES is used for the purpose of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, depression and insomnia. CES has been proposed as a possible treatment for headaches, fibromyalgia, smoking cessation and opiate withdrawal.
CES devices have two parts: the box to control the installation and the electrode set. The electrode position may vary, but some electrode arrangements have been cited by FDA-cleared devices, which can be viewed on the FDA website.
Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation - History
Low intensity electrical stimulation is believed to have originated in the studies of galvanic currents in humans and animals as conducted by Giovanni Aldini, Alessandro Volta and others in the 18th century. Aldini had experimented with galvanic head current as early as 1794 (upon himself) and reported the successful treatment of patients suffering from melancholia using direct low-intensity currents in 1804.
CES was initially studied for insomnia and called electrosleep therapy; it is also known as cranial-electro stimulation and transcranial electrotherapy.
Due to the rise of pharmaceutical treatments for depression, anxiety and insomnia, such as Prozac in the 1980s and Ambien in the 1990s, CES was not a well-known treatment for doctors and patients. During the mid-2000s, the combination of pharmaceutical brands becoming generic and Internet advertising caused CES devices to gain popularity. In 2011, the devices received media attention from the Wall Street Journal
Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation - Medical uses
In the United States, CES technology is classified by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a Class III medical device and must be dispensed by or on the order of a licensed healthcare practitioner, i.e., a physician, psychiatrist, nurse practitioner, psychologist, physician assistant, or occupational therapist who has an appropriate electrotherapy license, dependent upon state regulations. The United States requires a prescription for CES devices from a licensed healthcare practitioner. The FDA says that there are 11 CES devices cleared for marketing in the United States.In June 2014, the FDA announced that it "has determined that there is sufficient information to establish special controls, and that these special controls, together with general controls, will provide a reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness for CES devices. In this action, FDA is withdrawing the proposed rule and proposed order to call for PMAs [premarket approvals] for CES devices. FDA plans to issue a proposed order in the future for the reclassification of the CES device into class II."
Deep overview for CES works
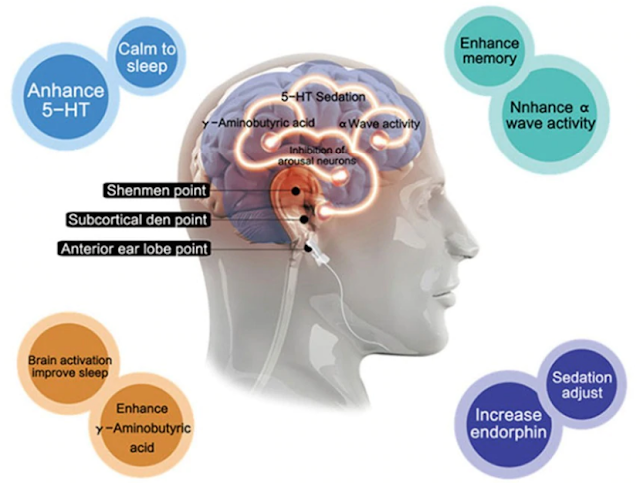
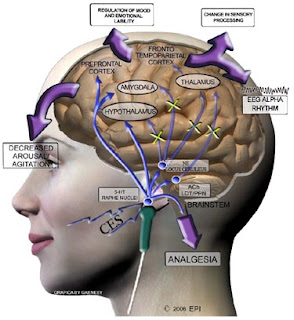
Electrodes are placed on the lobe of the ear, occipital junction, cymbal or temporal process.Despite the long history of CES, its basic principles and mechanisms are still unclear.
CES 1 mA stimulation (milliampere) has shown to reach the thalamic region at a radius of 13.30 mm. CES has shown to cause changes in the EEG, increasing relative alpha capacity and relative power reduction in delta and beta frequencies.
CES has also shown reaching the cortical and subcortical areas, in electromagnetic tomography and functional MRI studies.
CES treatments have been found to produce neurohormone changes and neurotransmitters associated with mental disorders: a significant increase in beta endorphin, adrenocorticotrophic and serotonin; Moderate increase in melatonin and norepinephrine, modest or inadequate increase in cholinesterase, gamma-aminobutyric acid and dehydroepiandrosterone and moderate cortisol reduction.
Overview of active CES:
- CES stimulates the brain to produce serotonin while lowering cortisol (a stress-causing hormone).
- Gently stimulates the brain to produce serotonin and other nerve chemicals responsible for healthy mood and sleep.
- allowing the brain to naturally produce serotonin while improving its ability.
- Adjust the limbic system of the brain. Proven in many published studies, this device has been cleared by FDA to treat depression, anxiety and insomnia, as well as chronic pain when used on the body.
References:
1. Cranial electrotherapy stimulation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cranial_electrotherapy_stimulation#cite_note-Rosa2017-1
2. Insomnia Treatment Device - Brand Name: ATANG


Post a Comment